On This Page
Telehealth opportunities cover a wide range of possible applications and services which can be profitably integrated into an existing or new practice.
Types of Telehealth Services
Examples include:
Live video conferencing, which allows healthcare providers to use telemedicine for real-time consultations with patients through video calls.
Store-and-forward systems enable healthcare providers to send patient information, such as images and test results, to specialists for review and consultation.
Remote patient monitoring involves healthcare providers tracking a patient’s health remotely using devices that monitor vital signs and other health data.
Mobile health apps allow patients to access healthcare services and information, including scheduling appointments, accessing medical records, and receiving virtual consultations.
Telepsychiatry offers mental health services remotely, including therapy sessions and psychiatric evaluations.
Telepharmacy provides remote pharmacy services, such as medication management, prescription refills, and consultations with pharmacists.
Telestroke services offer immediate consultation and diagnostic support for stroke patients in remote locations to ensure timely treatment.
Teledermatology allows for remote evaluation and diagnosis of skin conditions through video calls and image sharing using telemedicine software.
Teleconsultation offers virtual consultations with healthcare providers for non-emergency medical issues or follow-up appointments.
Teletriage involves remotely assessing patients to determine the urgency of their medical needs and provide appropriate guidance or referrals.
When Telehealth Is Not The Answer
When a face-to-face or more detailed physical examination or procedure is necessary, or the health concerns are potentially complex, Telehealth obviously has limitations.
It is recognized that the nature of Telehealth operations attract inherent diagnostic and treatment risks beyond traditional in-situ treatment settings.
It is crucial that standard operational procedures be reviewed for these risks, and that insurance coverages be carefully reviewed to avoid adverse risk assumptions and classifications.
Some practices may also encounter state-based multi-state licensing issues.
Key Components of A Successful Telemedicine Business Model
A number of core personal and organizational competencies can be identified which are the essential components of a successful Telehealth operation.
A telemedicine business relies on technology to conduct virtual consultations between healthcare providers and patients, utilizing a platform for video conferencing, secure messaging, and electronic health record integration.
Compliance with healthcare laws, such as HIPAA regulations, is essential for legal and ethical operation.
Healthcare providers offering telemedicine services must also be fully licensed. Licensed Telehealth practitioners must be licensed in the states where their patients are located, (potentially crossing many geographic boundaries) and have their qualifications verified.
Establishing a clear payment model and understanding reimbursement policies are crucial for financial sustainability.
Effective marketing strategies, quality care delivery, positive patient experiences, and strategic partnerships with healthcare providers are important for attracting and retaining patients.
Scalability and flexibility are also essential factors for long-term sustainability, requiring systematic adaptation to evolving technologies and regulations.
Legal, Regulatory And Compliance Aspects Of Telemedicine
Federal Regulations
The Social Security Act, particularly Section 1834(m), contains important provisions governing Medicare coverage of telehealth services.
Original requirements include limitations on eligible telehealth services, originating site requirements, provider qualifications, and technology specifications, but were extended as part of Covid-19 measures.
The extensions are valid through December 31, 2024 (at the time of writing). They allow telehealth services to be provided at any location where the patient is, including their home.
Additionally, more practitioners such as audiologists, occupational therapists, physical therapists, and speech-language pathologists are eligible to provide telehealth services.
The Act also extends the ability for Federally Qualified Health Centers and Rural Health Clinics to offer telehealth services, delays in-person requirements for mental health services via telehealth, and extends reimbursement for audio-only telehealth services.
Under the extensions, Telehealth can fulfill the face-to-face encounter requirement for hospice recertification, allowing nurse practitioners to provide comprehensive care.
The Act also includes provisions for a study on telehealth and Medicare program integrity, and extends safe harbor exceptions for telehealth services under high-deductible health plans, which is crucial for private practice.
For further on this, see the article: Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 Extends Telehealth Waivers
For information on the regulation of Telehealth more generally, see: Telehealth policy
Compliance Checklist
The compliance and regulatory requirements are numerous and can be complex.
Disclaimer: If you are setting up from scratch, the following may help to cover the bases, and is useful as a starting point. But this list is not exhaustive. Nor is it a substitute for professional advice.
Here’s a checklist of licensing and compliance requirements for healthcare practitioners setting up a telehealth operation in the USA:
Licensing Requirements
Obtain appropriate medical licenses:
- Get licensed in the state where you are located
- Obtain licenses for states where your patients are located
- Consider joining the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (IMLC) for expedited multi-state licensing
- Verify state-specific telehealth regulations:
- Check if your state offers special telehealth licenses
- Review any temporary or permanent telehealth waivers in effect
- Maintain active licenses and stay compliant with renewal requirements
Ensure HIPAA compliance:
- Review and ensure to undertake HIPAA-compliant technology and processes
- Obtain necessary Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
- Adhere to state-specific telehealth laws and regulations
Review and comply with online prescribing laws:
- Federal regulations for controlled substances
- State-specific prescribing rules
- Establish and document protocols for obtaining informed consent from patients
- Develop and document policies for verifying patient identity and location
Technology and Security
- Ensure selected telehealth platforms and tools are HIPAA-compliant
- Implement secure data storage and transmission methods and retain evidence of 3rd party compliance
- Establish and document protocols for protecting patient privacy and confidentiality
- Conduct and record outcomes of regular security risk assessments and document actions taken
Clinical Practice Standards
- Develop and document telehealth-specific clinical protocols and workflows
- Ensure adherence to applicable standards of care for telehealth
- Establish and document procedures for appropriate documentation and record-keeping
- Create and document protocols for handling emergencies during telehealth sessions
Billing and Reimbursement
- Verify and document telehealth coverage and reimbursement policies with payers
- Implement proper coding and billing procedures for telehealth services
- Stay informed about changes in telehealth reimbursement policies
Patient Education and Consent
- Develop patient education materials about telehealth services to support your telehealth practice.
- Create and implement informed consent processes for telehealth
- Include explicit procedures for discussing telehealth limitations with patients
Ongoing Compliance and Updates
- Stay informed about changes in telehealth laws and regulations
- Regularly review and update telehealth policies and procedures to comply with the latest telemedicine laws.
- Conduct periodic and ongoing training for staff on telehealth compliance, especially regarding the use of telemedicine technology.
- Monitor and adapt to evolving standards of care in telehealth
Telehealth regulations vary by state and change over time, so it is essential to remain in regular contact with legal experts to ensure compliance and risk minimization in your specific jurisdiction and circumstances.
Further information
For further reading on the regulations, see:
- Telehealth.HHS.gov
- Legal Requirements for Telehealth
- HIPAA Rules for telehealth technology
- 10 Things to Know About Telehealth Compliance
Malpractice Insurance
Providers offering telemedicine services should ensure that they have appropriate malpractice insurance coverage that includes telemedicine practice.
Insurers may have specific requirements for telemedicine coverage, so providers should review their telemedicine laws and make any necessary adjustments.
Key Success Factor: Your Telehealth Platform
Your chosen Telehealth platform is a key success factor, because it touches on the primary benefits of a remotely delivered service.
The benefits include:
1. Accessibility: The platform allows patients to easily access healthcare services from the comfort of their own homes, eliminating the need to travel to a physical clinic.
2. Convenience: The Telehealth platform allows patients to schedule appointments, receive medical advice, and access their health records all in one place, facilitating telemedicine visits.
3. Cost-effectiveness: Telehealth appointments should be cost-effective for both patients and healthcare providers compared to traditional in-person visits, making it easier to transfer to a telehealth mode. This is achieved without compromising patient care.
4. Improved patient outcomes: Patient outcomes are improved by enabling early intervention and regular monitoring of chronic conditions.
5. Scalability: Telehealth platforms are scalable, which allows for quick adaptation to changing (and increasing) patient needs and market demands.
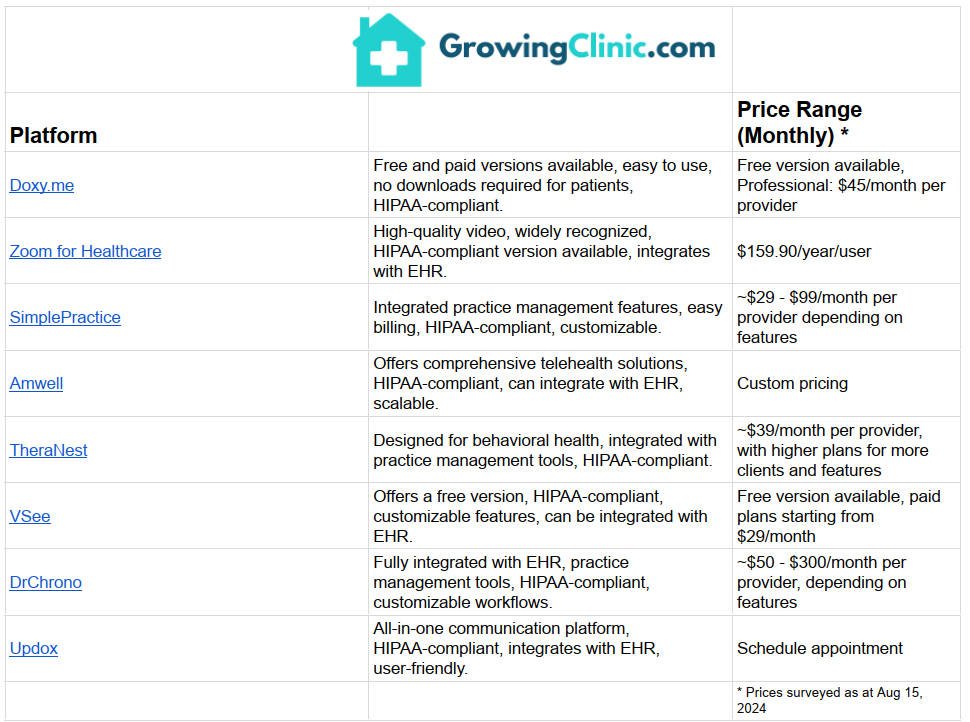
Popular Telehealth Platforms
When choosing your platform, you should take into account ease of use, affordability, compliance with healthcare regulations, integration with electronic health records, and features like video conferencing, messaging, and telehealth software for payment processing.
Here are some popular platforms you may wish to consider (not in order of recommendation):
How To Market Telehealth Services
Marketing telehealth services requires a strategic approach to reach and engage patients who may benefit from virtual healthcare options.
Here are some key steps to effectively market telehealth services:
Develop a comprehensive marketing plan
A detailed marketing plan outlines your goals, target audience, messaging, and marketing tactics. This plan should include a mix of digital and traditional marketing strategies to reach a wide range of potential patients.
Create a user-friendly website
Your website should be easy to navigate and provide clear information about your telehealth services.
Make sure to include a dedicated section highlighting the benefits of telehealth, how it works, and how patients can schedule an appointment.
Utilize search engine optimization (SEO)
Optimize your website and online content for search engines to increase visibility and attract more organic traffic for your telehealth practice.
Use relevant keywords related to telehealth services to improve your search engine rankings.
Leverage social media
Use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to promote your telehealth services.
Share educational content, patient testimonials, and information about upcoming telehealth appointments to engage with your audience.
Partner with local organizations
Collaborate with local healthcare organizations, community centers, and businesses to promote your telehealth services.
Consider hosting virtual events or webinars to educate the community about the benefits of telehealth.
Offer incentives
Encourage patients to try telehealth services by offering incentives such as discounts, promotional offers, or free consultations.
This can help attract new patients and drive more interest in your virtual healthcare options.
Collect and showcase patient testimonials
Highlight the positive experiences of patients who have used your telehealth services.
Testimonials can build trust and credibility with potential patients and help them feel more comfortable trying virtual healthcare.
Monitor and analyze results
Track the performance of your marketing efforts to understand what is working and what needs improvement.
Use analytics tools to measure website traffic, patient inquiries, and appointment bookings to optimize your marketing strategy.
Following these steps and implementing a well-rounded marketing plan, can promote your telehealth services and attract more patients.
Appointments And Scheduling Software For Telemedicine
Appointments and scheduling software for telemedicine allows healthcare providers to efficiently manage their virtual appointments with patients.
These software solutions typically include features such as:
Online booking
Patients can easily schedule appointments through a web-based platform, selecting their preferred date and time for the virtual consultation.
Automated reminders
Patients receive automated reminders via email or SMS to ensure they do not miss their telemedicine appointments.
Calendar integration
The software can sync with the healthcare provider’s calendar to avoid scheduling conflicts and double bookings of telemedicine visits.
Virtual waiting room
Patients can wait in a virtual waiting room before their appointment, where they can complete any necessary paperwork or forms.
Secure video conferencing
The software includes a secure video conferencing platform for conducting virtual consultations with patients.
E-prescriptions
Healthcare providers can electronically prescribe medications to patients during the telemedicine appointment.
Billing and payment processing
The software can handle billing and payment processing for telemedicine appointments, making it easy for healthcare providers to manage their finances.
Overall, appointments and scheduling software for telemedicine streamlines the process of managing virtual appointments, improving efficiency and patient satisfaction.
Iterative Improvements Of Your Telemedicine Services Rollout
Here are some steps to systemize the iterative improvements of your telemedicine services rollout:
Set clear goals and objectives
Define what you want to achieve with your telemedicine services rollout, such as increasing patient satisfaction, improving efficiency, or expanding access to care.
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs)
Identify metrics that will help you measure the success of your telemedicine services, such as patient engagement, appointment wait times, or revenue generated.
Implement feedback mechanisms
Collect feedback from patients, providers, and staff regularly to identify areas for telehealth practice improvement.
This can be done through surveys, interviews, or focus groups.
Prioritize improvements
Based on feedback and data collected, prioritize areas that need improvement and create a roadmap for implementing changes.
Test and iterate
Implement small changes or pilot programs to test improvements before rolling them out on a larger scale.
Gather feedback on these changes and iterate as needed.
Monitor and evaluate
Continuously monitor KPIs to track progress and evaluate the impact of improvements.
Use this data to make informed decisions about future changes.
Communicate updates
Keep stakeholders informed about the progress of the telemedicine services rollout and any improvements that have been implemented. This can help build trust and engagement among patients, providers, and staff.
Document processes
Create documentation for all aspects of the telemedicine services rollout, including workflows, protocols, and best practices.
This will help ensure consistency and efficiency in implementing improvements.
Train and educate staff
Provide training and education to staff on any new processes or technologies implemented as part of the telemedicine services rollout.
This will help ensure that everyone is on the same page and can effectively use the new tools.
Continuously improve
Treat the telemedicine services rollout as an ongoing process of improvement.
Stay agile and open to feedback, and be willing to make changes as needed to meet the evolving needs of patients and providers.
Telemedicine Business Startup Costs And Business Plan Example
Starting a telemedicine business can be financially rewarding.
However, like any business, it’s important to carefully plan and budget for startup costs.
Here is an example of telemedicine business startup costs and a basic business plan:
Startup Costs
Licensing and Legal Fees
$5,000 – This includes obtaining necessary licenses, permits, and legal fees for setting up a telemedicine business.
Technology Infrastructure
$10,000 – This includes setting up a secure telemedicine platform, acquiring necessary software, and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations.
Equipment and Supplies
$5,000 – This includes purchasing telemedicine technology such as cameras, microphones, and other necessary supplies to start a telemedicine practice.
Marketing and Advertising
$3,000 – This includes creating a website, social media presence, and other marketing efforts to start your own telemedicine business and attract patients.
Staffing Costs
$20,000 – This includes hiring healthcare providers, administrative staff, and IT support for your telemedicine business.
Insurance
$2,000 – This includes liability insurance and other necessary insurance coverage for your telemedicine business.
Total Startup Costs: $45,000
This is a prototype only as an example of the kinds of costs to consider. The actual numbers will vary significantly according to your circumstances.
Business Plan
Executive Summary
Provide an overview of your telemedicine business, including your mission, target market, and competitive advantage.
Market Analysis
Conduct market research to identify the demand for telemedicine services in your area and analyze your competitors’ telehealth business services..
Services Offered
Define the telemedicine services you will offer, such as virtual consultations, remote monitoring, or telepsychiatry.
Marketing Strategy
Outline your marketing plan, including how you will attract patients through online advertising, social media, and partnerships with healthcare providers.
Operations Plan
Describe how your telemedicine business will operate, including staffing, technology infrastructure, and patient scheduling.
Financial Projections
Create financial projections for your telemedicine business, including revenue forecasts, expenses, and break-even analysis.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that your telemedicine business complies with all healthcare regulations and data privacy laws.
By carefully planning and budgeting for startup costs, as well as creating a detailed business plan, you can increase the chances of success for your telemedicine business.
Telemedicine Services Startup Checklist
Starting a telemedicine services startup can be a complex process.
Here is a checklist to help you navigate the key steps involved in launching your telemedicine services startup:
1. Conduct Market Research
- Identify your target market and understand their needs and preferences.
- Research existing telemedicine services providers and assess their strengths and weaknesses.
- Determine the demand for telemedicine services in your target market.
2. Develop a Business Plan
- Define your business model, including the services you will offer, pricing strategy, and revenue streams.
- Outline your marketing and sales strategy to attract and retain customers.
- Create financial projections and a budget for your startup.
3. Obtain Necessary Licenses and Permits
- Research the legal requirements for offering telemedicine services in your jurisdiction.
- Obtain any necessary licenses and permits to operate your business legally.
4. Build a Telemedicine Platform
- Choose a telemedicine platform that meets your needs and budget.
- Customize the platform to reflect your brand and provide a seamless user experience.
- Ensure the platform complies with all relevant healthcare regulations and data security standards.
5. Recruit Healthcare Providers
- Hire licensed healthcare providers to deliver telemedicine services on your platform.
- Ensure your providers have the necessary qualifications and experience to deliver high-quality care.
- Train your providers on using the telemedicine platform and providing remote care effectively.
6. Establish Partnerships
- Collaborate with healthcare facilities, pharmacies, or other healthcare providers to expand your telehealth business offerings.
- Partner with insurers or employers to offer telemedicine services as part of their benefit packages.
- Build relationships with technology vendors and other service providers to support your operations.
7. Develop Marketing and Sales Strategies
- Create a marketing plan to promote your telemedicine services to your target audience and encourage them into your telehealth business.
- Utilize digital marketing channels, such as social media, search engine optimization, and email marketing, to reach potential customers.
- Develop partnerships with referral sources, such as healthcare providers or community organizations, to generate leads.
8. Implement Telemedicine Policies and Procedures
- Develop policies and procedures for providing telemedicine services, including patient consent, privacy, and security protocols.
- Ensure your providers follow best practices for delivering remote care and maintaining patient confidentiality.
- Establish protocols for handling emergencies and coordinating care with in-person providers.
9. Test and Launch Your Telemedicine Services
- Conduct a pilot program to test your telemedicine platform and services with a small group of users.
- Gather feedback from patients and providers to identify areas for improvement.
- Launch your telemedicine services to the public once you are confident in your platform and operations.
10. Monitor and Evaluate Performance
- Track key performance indicators, such as patient satisfaction, provider utilization, and revenue growth.
- Use data analytics to identify trends and opportunities for optimization.
- Continuously improve your telemedicine services based on feedback and data insights.

